It directs packets to MAC addresses. It handles VLAN tagging. It can even perform some Quality of Service (QoS) tasks. It’s also responsible for isolating network traffic to the virtual adapter that is supposed to be receiving it. When visualized, the Hyper-V network switch should be thought of in the same way as a standard switch. . Start Hyper-v Manager Start Administrative Tools Hyper-V Manager or run%ProgramFiles% Hyper-V virtmgmt.msc. From the Virtual Machines Pane select the machine you want then right click on it and select 'settings'. From the Settings for Machine Name pop-up window, select 'Network Adapter on the left pane. Now toggle the radio button Static under the dialog Box titled MAC Address in the right pane.
Important
This version of Virtual Machine Manager (VMM) has reached the end of support, we recommend you to upgrade to VMM 2019.
This article provides information about System Center - Virtual Machine Manager (VMM) default MAC addresses, and describes how to create and manage a custom MAC address pool.
VMM uses static MAC address pools to automatically generate and assign MAC address to VMs. This article describes default MAC address pools in the VMM fabric and explains how to create custom pools.
Default MAC address pool settings:
| MAC pool name | Environment | Default range |
|---|---|---|
| Default MAC address pool | Hyper-V | 00:1D:D8:B7:1C:00 – 00:1D:D8:F4:1F:FF |
| Default VMware MAC address pool | ESX/ESXi | 00:50:56:00:00:00 – 00:50:56:3F:FF:FF |
Before you start
Before you create a custom MAC pool note that:
- If you want to divide one of the default pools into smaller custom pools, you must first delete the default MAC address pool or the default VMware MAC address pool. You must delete the default pool to avoid duplicate MAC address assignments.
- The first three octets of the beginning and ending MAC address must be the same.
- You must enter a valid hexadecimal values between 00 and FF.
- The ranges that you specify cannot overlap.
- The address range must not have the multi-cast bit set to 1. For example, you cannot use addresses that start with X1, X3, X5, X7, X9, XB, XD, or XF, where X is any value.
- To avoid conflicts with addresses reserved by Microsoft, VMware, and Citrix, do not use the following prefixes:
- Reserved for Microsoft: 00:03:FF; 00:0D:3A; 00:12:5A; 00:15:5D; 00:17:FA; 00:50:F2; 00:1D:D8 (except for the 00:1D:D8:B7:1C:00 – 00:1D:D8:F4:1F:FF range that is reserved for VMM)
- Reserved for VMware: 00:05:69; 00:0C:29; 00:1C:14; 00:50:56 (except for the 00:50:56:00:00:00 – 00:50:56:3F:FF:FF range that is the reserved as the default VMware static range)
Create a custom pool
- Click Fabric > Networking > MAC Address Pools > Home > Show > Fabric Resources > Create > Create MAC Pool.
- In Create MAC Address Pool Wizard > Name and Host Group specify a name and description. In Host Group select the host groups that should use the pool.
- In MAC Address Range specify the start and end addresses.
- In Summary review the settings and click Finish. When the job shows as Completed verify pool in MAC Pools.
Release IP addresses
In some circumstances you might want to remove addresses from the MAC pool. For example if a host that was assigned an IP address during bare metal deployment is removed from VMM management, or if a VM goes into a missing state because it was removed outside VMM.
- Click Fabric > Networking > MAC Address Pools > Home > Show > Fabric Resources.
- In MAC Pools click the pool you want to modify > Properties.
- In Inactive addresses select the addresses you want to release.
Next steps
Learn about creating an IP address pool.
-->This article provides a solution to an issue that occurs when you start a guest virtual machine.
Original product version: Windows Server 2012 R2
Original KB number: 2804678
Symptoms
Consider the following scenario:
You have a Windows Server 2012 computer that is configured with the Hyper-V role. The Hyper-V server is configured to provide Dynamic MAC addresses to the guest machines.
When you start a guest virtual machine, you may encounter the following error message:
The application encountered an error while attempting to change the state of '<Virtual machine name>'
Synthetic Ethernet Port (Instance ID CCE417C5-BDD9-4216-85CA-248620EE75C6): Failed to power on with Error 'Attempt to access invalid address'.
On a Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V host, an Event ID 12565 from source 'Microsoft-Windows-Hyper-V-Worker' is logged, as described in the Event ID 12565 — NIC Configuration.
Cause
This problem occurs because the default number of dynamic MAC addresses for virtual machines (256) has been exceeded.
Hyper-V generates the MAC address as described below (mapping MAC address to aa-bb-cc-dd-ee-ff):
- The first three octets (aa-bb-cc) are Microsoft's IEEE organizationally Unique Identifier, 00:15:5D (which is common on all Hyper-V hosts.
- The next two octets (dd-ee) are derived from the last two octets of the server's IP address.
- The last octet (ff) is automatically generated from the range 0x0-0xFF.
Because the last octet is an 8-bit value, there is a default limit of 256 possible MAC addresses.

Resolution
Apply one of the following solutions:
Turn off the virtual machine, allocate a static MAC Address that does not belong to Hyper-V's dynamic MAC address range, then restart the virtual machine.
Increase the range of MAC addresses by using one of the following methods, by modifying the fifth and/or the sixth octet of the default dynamic MAC address range:
If the host is Windows Server 2008, you can modify the dynamic MAC address range via the following registry values:
HKLMSoftwareMicrosoftWindows NTCurrentVersionVirtualizationMinimumMacAddressHKLMSoftwareMicrosoftWindows NTCurrentVersionVirtualizationMaximumMacAddress
Note
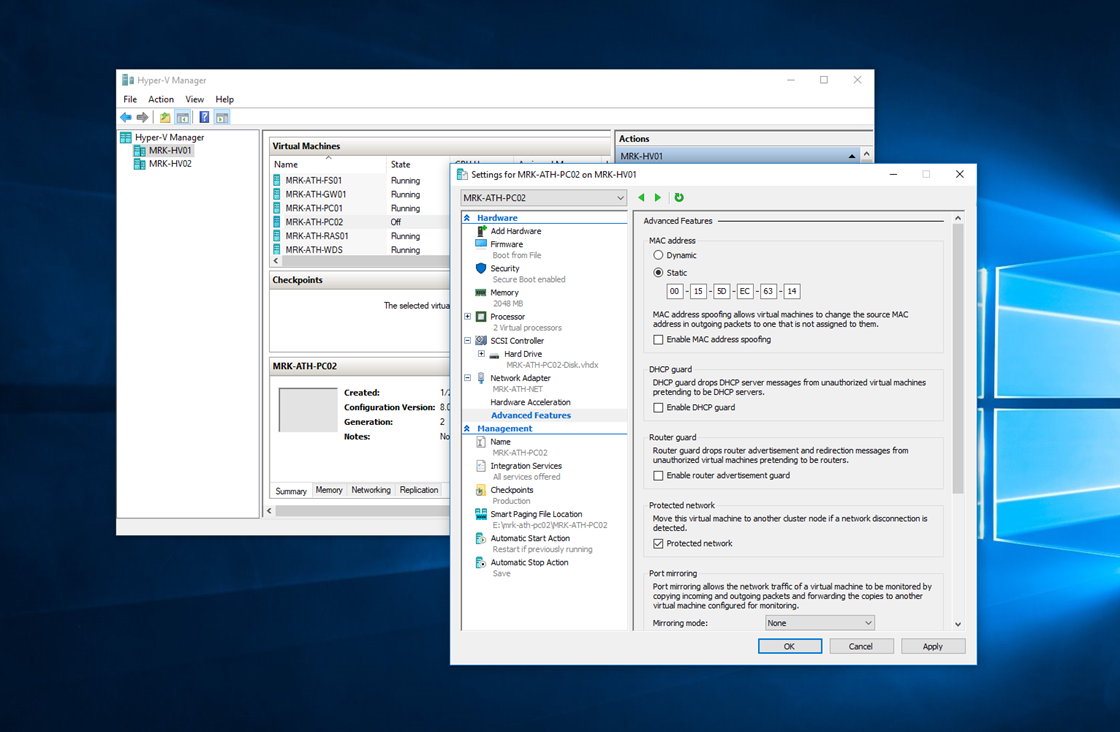
Hyper-v Set Static Mac Address
Knowledge of the hexadecimal numbering system is helpful to modify the octets. Each octet's range is 00 - FF.
More information
Hyper-v Mac Address Change
Refer to the following blog posts for additional reading on this subject:
